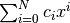fit
Note
Functions for fitting 2D data.
Module author: Adam Gagorik <adam.gagorik@gmail.com>
-
class fit.Fit(x, y, func, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
Base class for fitting.
| Parameters: |
- x (list) – array of x-values
- y (list) – array of y-values
- func (function) – function object
- popt (list) – initial guess for parameters
|
|---|
Warning
Do not explicitly create Fit instance, its a base class.
>>> fit = FitLinear([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
-
plot(xmin=None, xmax=None, xpoints=100, **kwargs)[source]
Wrapper around matplotlib.pyplot.plot(). Plots the fit line.
| Parameters: |
- xmin (float) – min x-value
- xmax (float) – max x-value
- xpoints (int) – number of xpoints
|
|---|
>>> fit = FitLinear([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
>>> fit.plot(xmin=-1.0, xmax=1.0, xpoints=10, lw=2, color='blue')
-
text(s, x, y=None, transform=None, rotate=False, draw_behind=True, **kwargs)[source]
Wrapper around matplotlib.pyplot.text(). Useful for putting
text along the fit line drawn by Fit.plot(), and rotating the
text using the derivative.
| Parameters: |
- s (str) – text
- x (float) – x-value of text
- y (float) – y-value of text; if None, use the fit line
- transform (matplotlib.transforms.Transform) – matplotlib transform; if None, plt.gca().transAxes
- rotate (bool) – rotate text using angle computed from derivative
- draw_behind (bool) – hide the plot objects behind the text
|
|---|
>>> fit = FitLinear([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
>>> fit.text('Hello!', 0.1, rotate=True, fontsize='large')
-
solve(y=0, x0=0, return_y=False, **kwargs)[source]
Wrapper around scipy.optimize.fsolve(). Solves y=fit(x) for x.
| Parameters: |
- y (float) – y-value
- x0 (float) – initial guess
- return_y (bool) – return x and fit(x)
|
|---|
| Returns: | xval, yval
|
|---|
>>> fit = FitLinear([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
>>> xval, yval = fit.solve(y=0, x0=1.0)
-
brute(a=0, b=1, find_max=False, return_y=False, **kwargs)[source]
Wrapper around scipy.optimize.brute(). Finds minimum in range.
| Parameters: |
- a (float) – lower x-bound
- b (float) – upper x-bound
- find_max (bool) – find max instead of min
- return_y (bool) – return x and fit(x)
|
|---|
| Returns: | xval, yval
|
|---|
>>> fit = FitLinear([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
>>> xval, yval = fit.brute(a=-1, b=1)
-
maxbrute(a=0, b=1, return_y=False, **kwargs)[source]
Calls Fit.brute() with find_max=True
-
minimize(x0=0, find_max=False, return_y=True, **kwargs)[source]
Wrapper around scipy.optimize.minimize(). Finds minimum using
a initial guess.
| Parameters: |
- x0 (float) – initial guess for x
- find_max (bool) – find max instead of min
- return_y (bool) – return x and fit(x)
|
|---|
| Returns: | xval, yval
|
|---|
>>> fit = FitLinear([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
>>> xval, yval = fit.minimize(x0=0.1)
-
maximize(x0, return_y=True, **kwargs)[source]
Calls Fit.minimize() with find_max=True
-
derivative(x, **kwargs)[source]
Wrapper around scipy.misc.derivative(), unless an inheriting
class implements the derivative analytically.
| Parameters: | x (float) – x-value to evaluate derivative at |
|---|
| Returns: | float |
|---|
-
tangent(x, **kwargs)[source]
Compute a tangent line at x.
| Parameters: |
- x (float) – x-value to evaluate derivative at
- xmin (float) – min x-value
- xmax (float) – max x-value
- xpoints (int) – number of xpoints
|
|---|
>>> fit = FitLinear([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
>>> func = fit.tangent(x=1.5)
>>> print func(1.5)
... 0.0
-
plot_tangent(x, xmin=None, xmax=None, xpoints=100, **kwargs)[source]
Plot a tangent line at x.
| Parameters: |
- x (float) – x-value to evaluate derivative at
- xmin (float) – min x-value
- xmax (float) – max x-value
- xpoints (int) – number of xpoints
|
|---|
>>> fit = FitLinear([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
>>> fit.plot_tangent(x=1.5, lw=2, color='blue')
-
summary()[source]
Create a summary dict of fit results.
-
sort(**kwargs)[source]
Sort x and y values.
-
class fit.FitPower(x, y, order=1, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
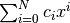
| Parameters: | order (int) – order of polynomial |
|---|
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitLinear(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
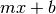
-
derivative(x, **kwargs)[source]
analytic derivative of function
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitQuadratic(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
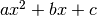
-
derivative(x, **kwargs)[source]
analytic derivative of function
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitInterp1D(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None, **kwargs)[source]
Fit to interpolating function.
| Parameters: | kind (str) – linear, nearest, zero, slinear, quadratic, cubic. |
|---|
kind : linear, nearest, zero, slinear, quadratic, cubic
-
class fit.FitUnivariateSpline(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None, **kwargs)[source]
Fit to spline.
| Parameters: | k – degree of spline (<=5) |
|---|
-
class fit.FitLagrange(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
Fit to lagrange interpolating spline. It sucks.
-
class fit.FitBarycentric(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None, **kwargs)[source]
Fit to lagrange interpolating spline. It sucks.
-
class fit.FitTanh(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
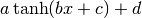
-
derivative(x, **kwargs)[source]
analytic derivative of function
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitLog(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
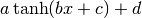
-
derivative(x, **kwargs)[source]
analytic derivative of function
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitXTanh(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
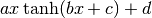
-
derivative(x, **kwargs)[source]
analytic derivative of function
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitErf(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
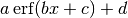
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitXErf(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
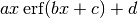
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitGaussian(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
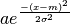
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitSin(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
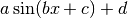
-
derivative(x, **kwargs)[source]
analytic derivative of function
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitCos(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
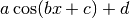
-
derivative(x, **kwargs)[source]
analytic derivative of function
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitLinearZero(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
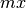
-
derivative(x, **kwargs)[source]
analytic derivative of function
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict
-
class fit.FitQuadraticZero(x, y, popt=None, yerr=None)[source]
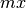
-
derivative(x, **kwargs)[source]
analytic derivative of function
-
summary()[source]
create a summary dict